Learn DAN prototxt
About DAN
DAN (Deep Adaptation Network) was proposed to learn transferable features which generalize well to novel tasks for Domain Adaptation. In DAN, hidden representa- tions of all task-specific layers are embedded in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space where the mean embeddings of different domain distributions can be explicitly matched. The domain discrepancy is further reduced using an optimal multi-kernel selection method for mean embedding matching.[1]
Here is the main structure of DAN.
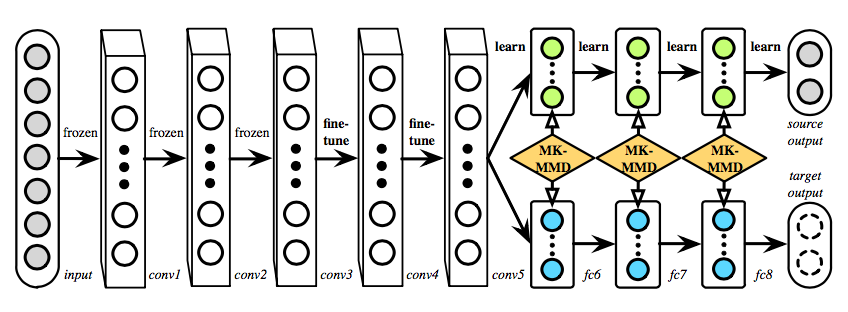
Since deep features eventually transition from general to specific along the network, (1) the features extracted by convolutional layers conv1–conv3 are general, hence these layers are frozen, (2) the features extracted by layers conv4–conv5 are slightly less transferable, hence these layers are learned via fine-tuning, and (3) fully connected layers fc6–fc8 are tailored to fit specific tasks, hence they are not transferable and should be adapted with MK-MMD.
Following we will detail the *.prototxt file of DAN.
train_val.prototxt
name: "amazon_to_webcam"
layer { # source domain data layer
name: "source_data"
type: "ImageData" # 直接使用 Raw Image 作为输入
top: "source_data"
top: "lp_labels"
image_data_param {
source: "./data/office/amazon_list.txt"
batch_size: 64
shuffle: true
new_height: 256
new_width: 256
}
transform_param { # 进行数据的转换
crop_size: 227
# 如果我们输入的图片尺寸大于crop_size,那么图片会被裁剪。
# 当 phase 模式为 TRAIN 时,裁剪是随机进行裁剪
# 而当为TEST 模式时,其裁剪方式则只是裁剪图像的中间区域。
mean_file: "./data/ilsvrc12/imagenet_mean.binaryproto"。
# 图片减去均值再训练,会提高训练速度和精度。因此,一般都会提供数据集的均值文件。
mirror: true # mirror可以产生镜像,弥补小数据集的不足
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
layer { # target domain data layer
name: "target_data"
type: "ImageData"
top: "target_data"
top: "target_label"
image_data_param {
source: "./data/office/webcam_list.txt"
batch_size: 64
shuffle: true
new_height: 256
new_width: 256
}
transform_param {
crop_size: 227
mean_file: "./data/ilsvrc12/imagenet_mean.binaryproto"
mirror: true
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
layer { # silence layeris simply to avoid that the output of unused blobs is reported in the log.
name: "target_label_silence"
type: "Silence"
bottom: "target_label"
include: { phase: TRAIN}
}
layer { # target data layer for test. So `mirror` is set to false.
name: "target_data"
type: "ImageData"
top: "data"
top: "lp_labels"
image_data_param {
source: "./data/office/webcam_list.txt"
batch_size: 1
shuffle: true
new_height: 256
new_width: 256
}
transform_param {
crop_size: 227
mean_file: "./data/ilsvrc12/imagenet_mean.binaryproto"
mirror: false
}
include: { phase: TEST }
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- source and target data concatenation
layer {
name: "concat_data"
type: "Concat"
bottom: "source_data"
bottom: "target_data"
top: "data"
concat_param {
concat_dim: 0
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- convolution
### layer { # output h_o = (h_i + 2 * pad_h - kernel_h) / stride_h + 1
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param { # learning rate and decay multipliers for the filters
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param { # learning rate and decay multipliers for the biases
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 96 # number of filters
kernel_size: 11 # kernel size
stride: 4
weight_filler { # parameter for weight initialization
type: "gaussian" # initialize the filters from a Gaussian
std: 0.01 # distribution with stdev 0.01 (default mean: 0)
}
bias_filler { # parameter for bias initialization
type: "constant"
value: 0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "conv1"
}
layer { # 局部响应归一化层完成一种“临近抑制”操作,对局部输入区域进行归一化。
name: "norm1"
type: "LRN"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "norm1"
lrn_param {
local_size: 5
alpha: 0.0001
beta: 0.75
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "norm1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 3
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
pad: 2
kernel_size: 5
group: 2
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.01
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "conv2"
}
layer {
name: "norm2"
type: "LRN"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "norm2"
lrn_param {
local_size: 5
alpha: 0.0001
beta: 0.75
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "norm2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 3
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "conv3"
param {
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 384
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.01
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu3"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv3"
top: "conv3"
}
layer {
name: "conv4"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv3"
top: "conv4"
param {
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 384
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
group: 2
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.01
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu4"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv4"
top: "conv4"
}
layer {
name: "conv5"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv4"
top: "conv5"
param {
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
group: 2
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.01
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu5"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv5"
top: "conv5"
}
layer {
name: "pool5"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv5"
top: "pool5"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 3
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "fc6"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool5"
top: "fc6"
param {
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 4096
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.005
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu6"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc6"
}
layer { # Dropout层在激活之后
name: "drop6"
type: "Dropout"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc6"
dropout_param {
dropout_ratio: 0.5
}
}
layer {
name: "fc7"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc7"
param {
lr_mult: 1
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
decay_mult: 0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 4096
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.005
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu7"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc7"
}
layer {
name: "drop7"
type: "Dropout"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc7"
dropout_param {
dropout_ratio: 0.5
}
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- alias fc7 to source_features_fc7 in test
layer { # The Split layer is a utility layer that splits an input blob to multiple output blobs. This is used when a blob is fed into multiple output layers.
name: "fc7_alias"
type: "Split"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "source_features_fc7"
include: { phase: TEST }
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- split source and target in train
layer { # 与split layer的不一样在于split的作用是将bottom复制多份,输出到tops.
name: "slice_features_fc7"
type: "Slice"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "source_features_fc7"
top: "target_features_fc7"
slice_param {
slice_dim: 0
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- fc8 of source
layer {
name: "fc8_source"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "source_features_fc7"
top: "source_features_fc8"
param {
name: "fc8_w"
lr_mult: 10
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "fc8_b"
lr_mult: 20
decay_mult: 0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 31
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.01
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "accuracy"
type: "Accuracy"
bottom: "source_features_fc8"
bottom: "lp_labels"
top: "lp_accuracy"
include: { phase: TEST }
}
layer {
name: "softmax_loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "source_features_fc8"
bottom: "lp_labels"
top: "softmax_loss"
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- fc8 of target
layer {
name: "fc8_target"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "target_features_fc7"
top: "target_features_fc8"
param {
name: "fc8_w"
lr_mult: 10
decay_mult: 1
}
param {
name: "fc8_b"
lr_mult: 20
decay_mult: 0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 31
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.01
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0
}
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------- mmd of fc7 and fc8
layer {
name: "mmd_loss_fc7"
type: "MMDLoss"
bottom: "source_features_fc7"
bottom: "target_features_fc7"
top: "fc7_mmd_loss"
loss_weight: 1
mmd_param {
kernel_num: 5
kernel_mul: 2.0
fix_gamma: false
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
layer {
name: "mmd_loss_fc8"
type: "MMDLoss"
bottom: "source_features_fc8"
bottom: "target_features_fc8"
top: "fc8_mmd_loss"
loss_weight: 1
mmd_param {
kernel_num: 5
kernel_mul: 2.0
fix_gamma: false
}
include: { phase: TRAIN }
}
solver.prototxt
net: "./models/DAN/amazon_to_webcam/train_val.prototxt"
test_iter: 795
test_interval: 300 # 测试间隔。也就是每训练300次,才进行一次测试。
base_lr: 0.0003 # 基础学习率
lr_policy: "inv" # 学习率调整的策略
gamma: 0.002
power: 0.75
momentum: 0.9 # 上一次梯度更新的权重,用来加权之前梯度方向对现在梯度下降方向的影响.
display: 100
max_iter: 50000
snapshot: 60000
snapshot_prefix: "./models/DAN/amazon_to_webcam/trained_model"
solver_mode: GPU
snapshot_after_train: false
test_iter:
这个要与test layer中的batch_size结合起来理解。mnist数据中测试样本总数为10000,一次性执行全部数据效率很低,因此我们将测试数据分成几个批次来执行,每个批次的数量就是batch_size。假设我们设置batch_size为100,则需要迭代100次才能将10000个数据全部执行完。因此test_iter设置为100。在这里,batch_size=1,所以test_iter是总数795。
lr_policy:
- fixed: 保持base_lr不变.
- step: 如果设置为step,则还需要设置一个stepsize, 返回
base_lr*gamma^(floor(iter/stepsize)),其中iter表示当前的迭代次数 - exp: 返回
base_lr * gamma ^ iter,iter为当前迭代次数 - inv: 如果设置为inv,还需要设置一个power, 返回
base_lr * (1 + gamma * iter) ^ (- power) - multistep: 如果设置为multistep,则还需要设置一个stepvalue。这个参数和step很相似,step是均匀等间隔变化,而multistep则是根据stepvalue值变化
- poly: 学习率进行多项式误差, 返回
base_lr (1 - iter/max_iter) ^ (power) - sigmoid: 学习率进行sigmod衰减,返回
base_lr ( 1/(1 + exp(-gamma * (iter - stepsize))))
Refenrence
[1] Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. 2015: 97-105.